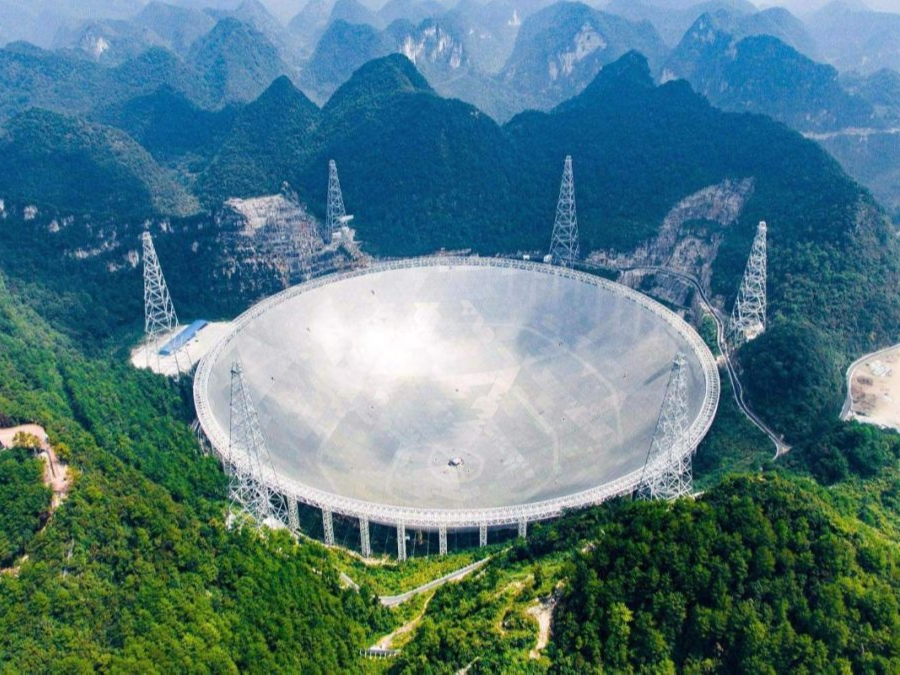

- On January 11, 2020, China Tianyan's national major science and technology infrastructure FAST was officially opened for operation.
On January 11, 2020, the 500-meter-diameter spherical radio telescope (FAST), known as China Tianyan, officially opened for operation through national acceptance, and became the world's largest and most sensitive radio telescope. It also means that humans are exploring the unknown areas of the universe. His eyesight is deeper and his vision is wider.
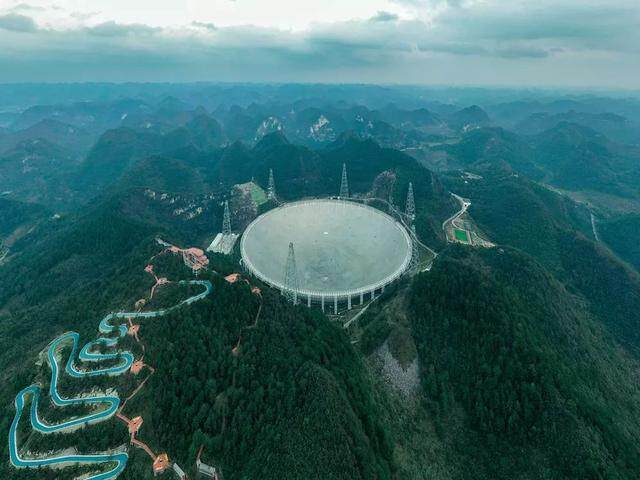

Two, 11, 43, 93, 102 ... From the first discovery of 2 pulsars by China Tianyan in October 2017, to the national acceptance meeting held on the 11th, it was announced that 102 pulsars have been found, which is two years The number of pulsars discovered more than the sum of the number of pulsar search teams in Europe and the United States in the same period.

FAST is the world's largest single-aperture radio telescope built in Pingtang County, Guizhou Province. During the construction process, it overcomes the technical problems of the telescope's huge volume and ultra-high precision. Experts of the National Acceptance Committee believe that China Tianyan's various indicators have reached or exceeded the approved acceptance indicators, and some key technologies have reached the international leading level.
Four Characteristics of Chinese Tianyan Body Shape
Large: The reflecting surface is composed of 4,450 reflecting units with a total area of 250,000 square meters, which is equivalent to 30 standard football fields.
Qiao: The 30-ton feed tank is controlled by 6 steel cables and can be positioned in real time at a height of 140 meters and a scale of 206 meters.
Strong: Can see more distant and faint celestial bodies. It can find stars in 1 minute. Even if the coordinates are provided to a radio telescope with a diameter of 100 meters, it will take 9 minutes to see the other party.
Fine: The measurement angle on a 500-meter scale is accurate to 8 arc seconds, and the positioning accuracy of 10 mm requires a maximum of 3.8 mm.
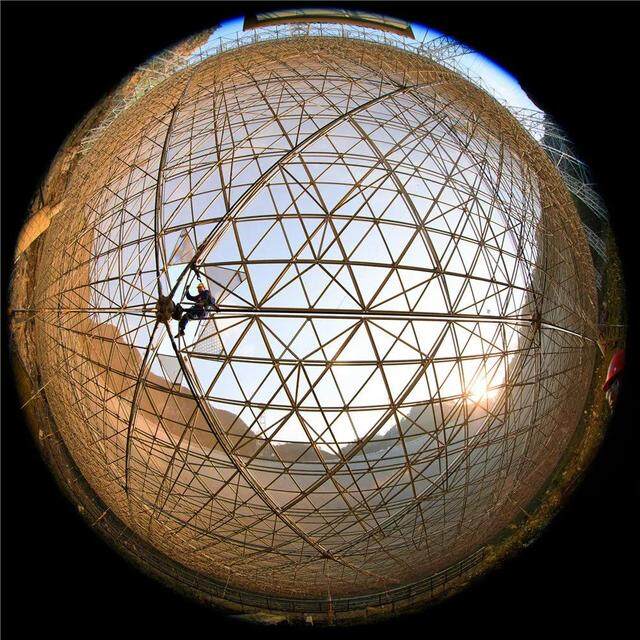
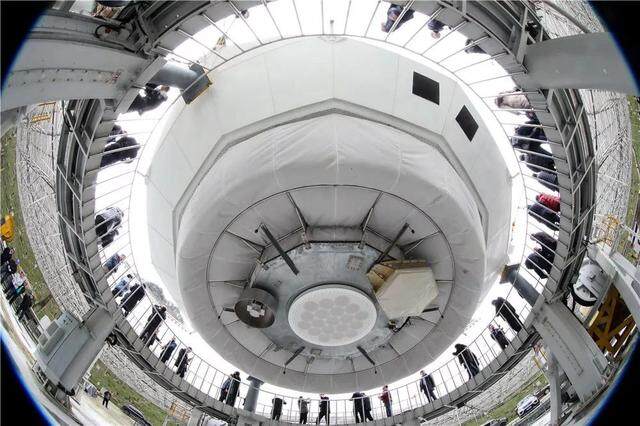
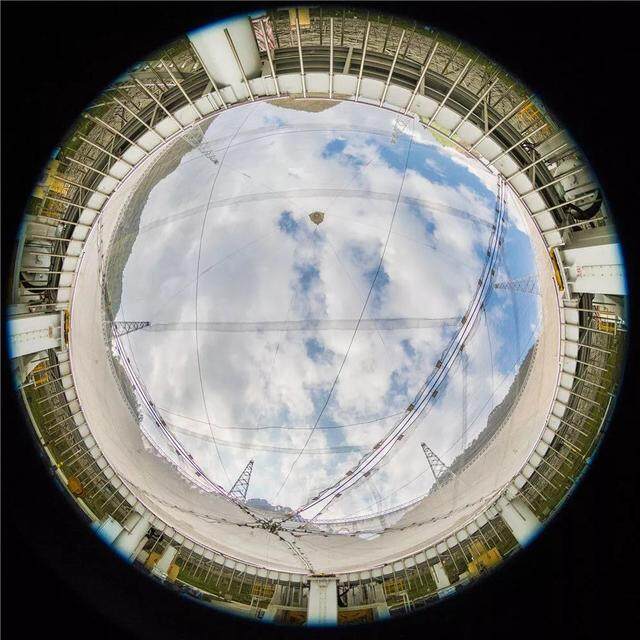



China Sky Eye (FAST) is an idea proposed by the older generation of astronomers represented by Nan Rendong in the 1990s to build the world's largest single-aperture radio telescope using the natural karst giant depression in Guizhou Province. After 5 and a half years of hard construction, the FAST team has overcome the technical problems of super-large scale and ultra-high precision of the telescope, and completed the project construction task on schedule with high quality. FAST was commissioned on September 25, 2016 and entered the commissioning period.
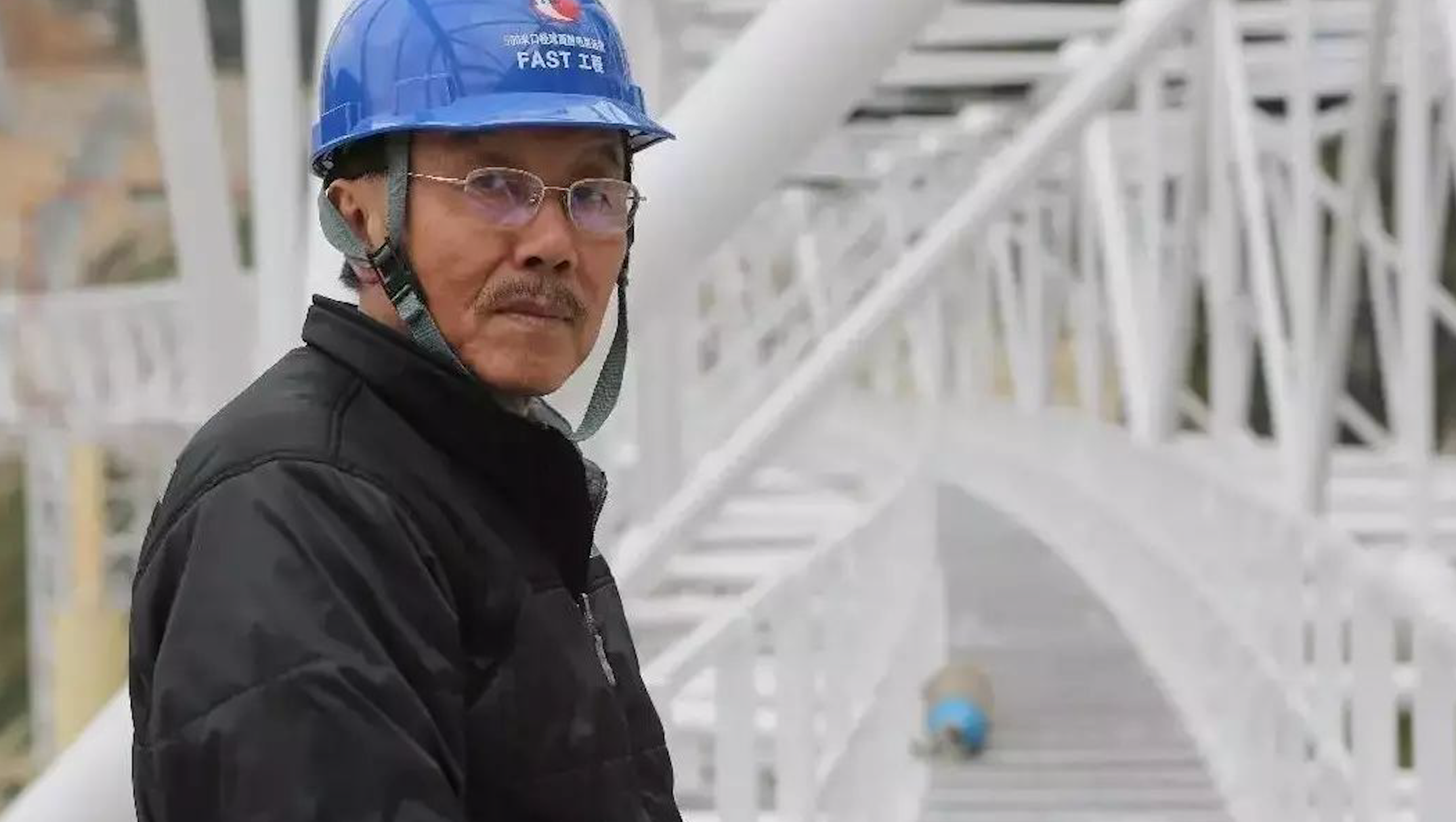

Since FAST was completed and launched in 2016, why was it accepted today? In fact, it is not easy for the telescope to realize the various observation intentions of the scientists and achieve stable and reliable sensitivity. The debugging period of the traditional international large radio telescope is generally no less than 4 years, and the huge receiving area of FAST makes its structural system more complicated. After two years of intensive debugging work, the FAST team realized a variety of observation modes such as tracking, drift scanning, and scanning in motion. Several key indicators exceeded expectations. They passed the process acceptance in April 2019 and were opened to domestic astronomers. At present, the range of FAST observations can reach the outer margins of galaxies beyond the galaxy and even 10 billion light years.
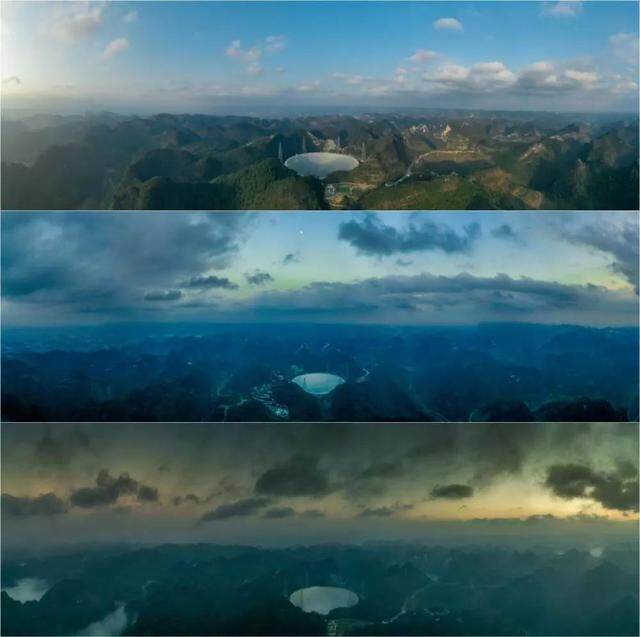

Since the FAST test run, the facility has been operating stably and reliably, with a sensitivity more than 2.5 times that of the world's second largest single-aperture radio telescope. This is the first time that a radio telescope built in China has occupied a commanding height in the main performance indicators.
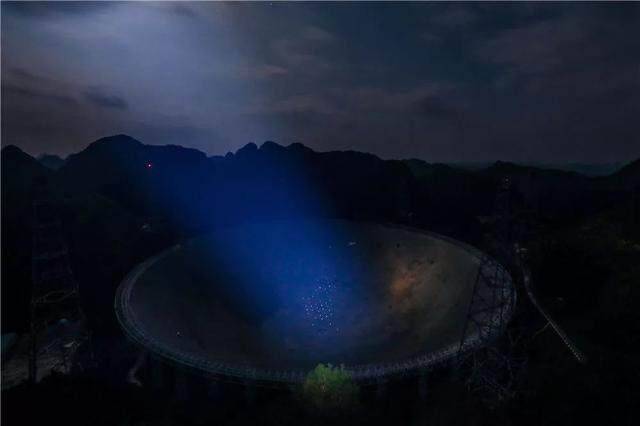

With the improvement of performance, the scientific potential of FAST has begun to appear. Currently, 146 qualified pulsar candidates have been detected, of which 102 have been certified. FAST has achieved polarization calibration and has used innovative methods to detect the Milky Way's interstellar magnetic field. In the next 3-5 years, the high sensitivity of FAST will likely lead to breakthroughs in the frontier directions of low-frequency gravitational wave detection, the origin of fast radio storms, and interstellar molecules. The National Astronomical Observatory is further actively organizing relevant experts at home and abroad to study how to use the excellent performance of FAST, strengthen openness and sharing at home and abroad, promote the output of major results, and bravely climb the world's scientific and technological peak.
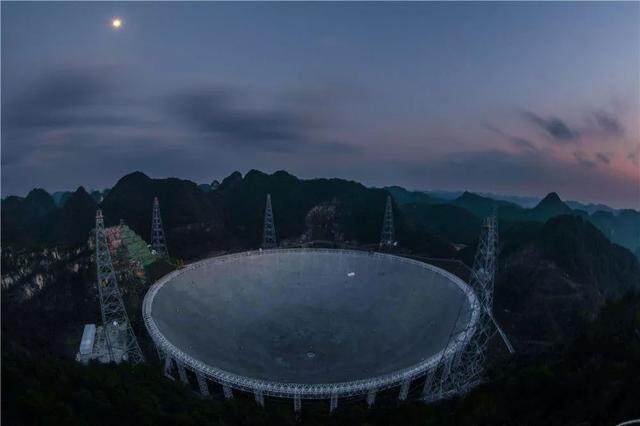

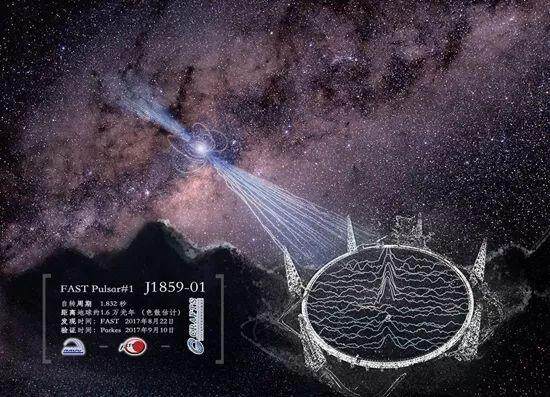

As the world's largest and most sensitive radio telescope, China Tianyan Project has come to a successful conclusion. It means that China's major scientific and technological infrastructure has been further improved, and human beings have a deeper perspective on exploring the unknown universe. Editor / Zhao Yongjing
Comment
 Praise
Praise
 Collect
Collect
 Comment
Comment
 Search
Search














Write something~